4.1. Report Data Structure
The Report structure tab of the report editor is described below:
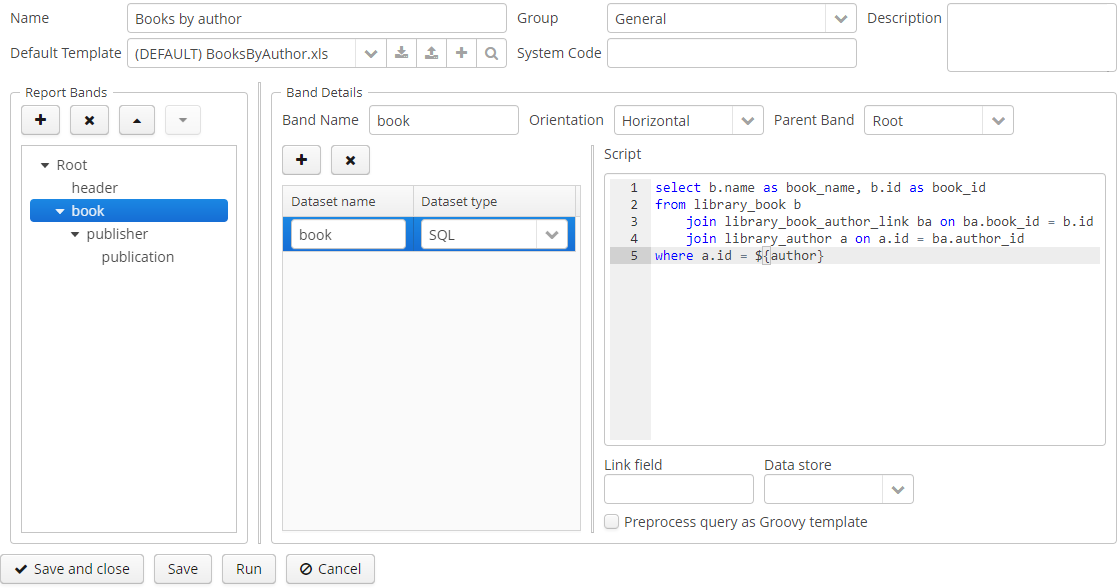
The top part contains fields to enter general report properties:
-
Name – report name. The name can be localized in the Localization tab.
-
Group – report group, which is used for grouping in the standard report browser.
-
Default template – report output template.
-
System code – optional code, which you may use to identify the report in the application code.
The main element of the report data structure is the band hierarchy – Report bands.
A report band has the following parameters:
-
Band name – unique band name within the report. It must contain only Latin letters, numbers and underscores. Moreover, if the band name starts with header, its data will not be printed in the table output.
-
Orientation – band orientation: Horizontal, Vertical or Crosstab. Horizontal bands are copied downwards, vertical – to the right, crosstab – to the right and downwards as a matrix. Horizontal bands may contain sub-bands.
-
Parent band – parent band.
Each band includes one or more datasets. At the moment when a report is run, datasets are transformed into lists of rows, where each row contains a map of name-value pairs. A band appears in the report as many times as there are rows in its longest dataset. Field names are specified in the report template and are replaced with corresponding values from the dataset when the report is produced. When describing datasets, you can use external parameters of the report as well as fields from other bands – this allows creating linked bands.
Each report has the Root band. You can create datasets in it and refer to their fields from other bands, but you cannot use the Root band in the report template.
The Dataset name column value is used for user convenience only.
The Link field is used to merge data from multiple datasets inside one band. It can be used when the whole data for the report row could not be received by a single query or a Groovy script.
Supported dataset types are described below.