4.3. External Report Parameters
External parameters are passed from the outside when running a report and can be used as conditions in datasets. All external parameters become fields for each report band, so you can use them directly in the template as dataset fields. If any dataset contains field with the same name, it overrides the external parameter in the corresponding band and the report uses the dataset field value.
You can describe the external parameters in the Parameters and Formats tab of the report editor. The form for adding parameters is provided below:
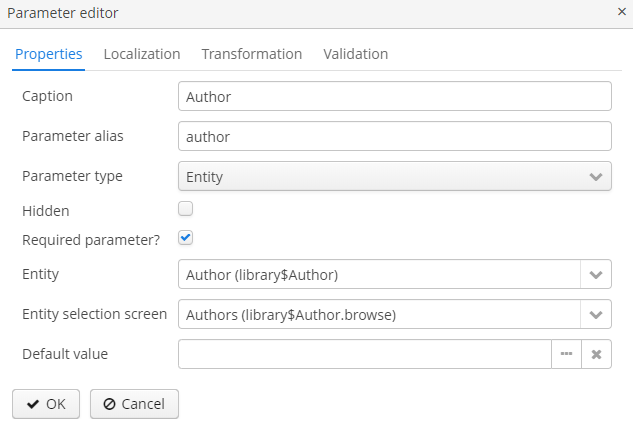
Properties tab:
-
Caption – parameter name, as it will appear in the parameter input form when running the report.
-
Parameter alias – parameter alias used to access it in datasets.
-
Parameter type – parameter type.
-
Hidden – flag that defines whether the request for parameter should be hidden from users.
-
Required parameter? – flag determining if the parameter is mandatory.
-
Entity – if the Entity or List of entities parameter type is selected, then you need to select the entity type in this field.
-
Entity selection screen – optional screen identifier, which will be used to select entity instances. If the screen is not specified, selection will be made from a special screen generic for all entities.
-
Enumeration – if the Enumeration parameter type is specified, then you need to select the enumeration type in this field.
-
Default value – defines the parameter value that will be used by default if no other value is selected by the user.
-
Default date(time) is current – if the temporal parameter type is specified (
Date,TimeorDate and time), this flag defines whether the current timestamp will be used as the default parameter value.
In the Localization tab, you can define the parameter name for different locales. In order to do this, you should enter the locale_name = parameter_name pairs, for example:
ru = Книга- Input parameters transformation
-
The Transformation tab allows you to apply a Groovy script on the parameter before using it in the report.
A Groovy script should return new parameter value. Current parameter value is available in the script by the
paramValuealias, the parameters map is available by aliasparams. For example:return "%" + paramValue + "%"You can also use one predefined transformations that add wildcards for text (String) parameters:
-
Starts with, -
Ends with, -
Contains.
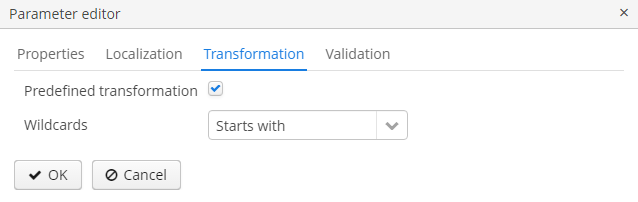 Figure 54. Input parameters transformation
Figure 54. Input parameters transformation -
In the Validation tab, you can define a Groovy script with some condition for the parameter validation, see the details below.
- Input parameters validation
-
You can validate an input parameter and/or define the cross-parameter validation.
-
You can enable validation of each parameter in the Validation tab of the parameter editor by checking the Validate checkbox. The validation logic is specified by a Groovy script. The script should check the parameter value and call the
invalid()method if the value is not valid. This method will show the user an alert with the given message about the report validation errors.The following variables are passed into the script:
-
value– the parameter value entered by the user. -
dataManager– an object of theDataManagertype that provides CRUD functionality. -
metadata– an object of theMetadatatype that provides access to the application metadata. -
security– an object of theSecuritytype used to check user access rights to different objects in the system. -
userSession– an object of theUserSessiontype associated with the currently authenticated user.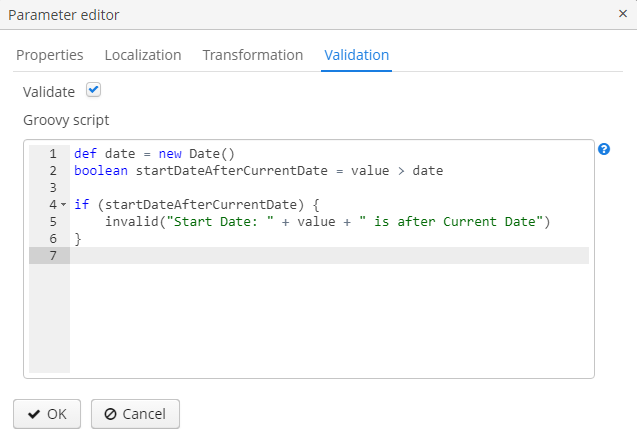 Figure 55. Input parameters validation
Figure 55. Input parameters validation
-
-
Cross-parameter validation can be enabled by checking the Validate checkbox in the Cross parameters validation section of the Parameters and Formats tab. The validation logic is specified by a Groovy script. The script should check whether or not parameter values make sense in relation to each other and call the
invalid()method if they do not. This method will show the user an alert with the given message about the report validation errors.In addition to the variables listed above, the
paramsvariable is passed into the script to access the external report parameters map.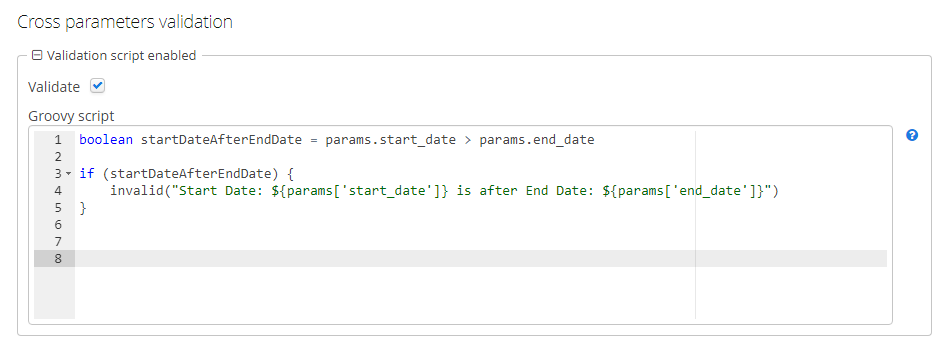 Figure 56. Cross-parameter validation
Figure 56. Cross-parameter validation
-