3.9.1. Dynamic Attributes
Dynamic attributes are additional entity attributes, that can be added without changing the database schema and restarting the application. Dynamic attributes are usually used to define new entity properties at deployment or production stage.
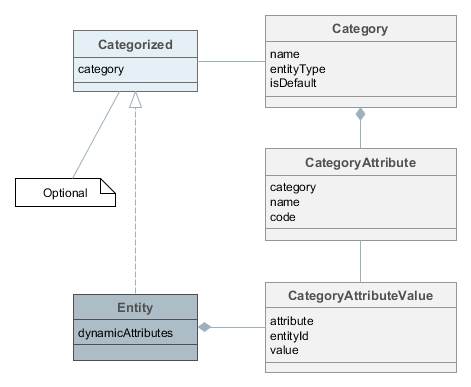
CUBA dynamic attributes implement the Entity-Attribute-Value model.
-
Category- defines a category of objects and the corresponding set of dynamic attributes. The category must be assigned to some entity type.For example, there is an entity of the Car type. We can define two categories for it: Truck and Passenger. The Truck category will contain Load Capacity and Body Type attributes, and the Passenger category – Number of Seats and Child Seat.
-
CategoryAttribute- defines a dynamic attribute related to some category. Each attribute describes a single field of a definite type. The requiredCodefield contains the system name of the attribute. TheNamefield contains the human-readable attribute name. -
CategoryAttributeValue- dynamic attribute value for a particular entity instance. Dynamic attribute values are physically stored in the dedicatedSYS_ATTR_VALUEtable. Each table record has a reference to some entity (ENTITY_IDcolumn).
An entity instance can have dynamic attributes of all categories related to the entity type. So if you create two categories of the Car entity mentioned above, you will be able to specify any dynamic attribute from both categories for a Car instance. If you want to be able to classify an entity instance as belonging to a single category (a car can be either truck or passenger), the entity must implement Categorized interface. In this case an entity instance will have the reference to a category, and dynamic attributes from this category only.
Loading and saving of dynamic attribute values is handled by DataManager. The setLoadDynamicAttributes() method of LoadContext and the dynamicAttributes() method of the fluent API are used to indicate that dynamic attributes should be loaded for entity instances. By default, dynamic attributes are not loaded. At the same time, DataManager always saves dynamic attributes contained in entity instances passed to commit().
Dynamic attribute values are available through getValue() / setValue() methods for any persistent entity inherited from BaseGenericIdEntity. An attribute code with the + prefix should be passed to these methods, for example:
Car entity = dataManager.load(Car.class).id(carId).dynamicAttributes(true).one;
Double capacity = entity.getValue("+loadCapacity");
entity.setValue("+loadCapacity", capacity + 10);
dataManager.commit(entity);In fact, the direct access to attribute values in the application code is rarely needed. Any dynamic attribute can be automatically displayed in any Table or Form component bound to a data container with the entity for which the dynamic attribute was created. The attribute editor described in the next section allows you to specify screens and components that should show the attribute.
User permissions to access dynamic attributes can be set in the security role editor in the same way as for regular attributes. Dynamic attributes are displayed with the + prefix.