5.3.4. WAR deployment to Tomcat Windows Service
-
Use the CUBA project tree > Project > Deployment > WAR Settings dialog in Studio or just manually add the buildWar task to the end of build.gradle:
task buildWar(type: CubaWarBuilding) { appHome = '${app.home}' singleWar = true includeContextXml = true includeJdbcDriver = true appProperties = ['cuba.automaticDatabaseUpdate': true] }If the target server parameters differ from what you have on the local Tomcat used for fast deployment, provide appropriate application properties. For example, if the target server runs on port 9999 and you build separate WARs, the task definition should be as follows:
task buildWar(type: CubaWarBuilding) { appHome = '${app.home}' singleWar = false includeContextXml = true includeJdbcDriver = true appProperties = [ 'cuba.automaticDatabaseUpdate': true, 'cuba.webPort': 9999, 'cuba.connectionUrlList': 'http://localhost:9999/app-core' ] }You can also specify a separate
context.xmlfile to setup the connection to the production database or provide that file later on the server:task buildWar(type: CubaWarBuilding) { appHome = '${app.home}' singleWar = true includeContextXml = true includeJdbcDriver = true appProperties = ['cuba.automaticDatabaseUpdate': true] coreContextXmlPath = 'modules/core/web/META-INF/war-context.xml' } -
Run the
buildWarGradle task. As a result,app.warfile (or several files if you build separate WARs) will be generated in thebuild/distributionsdirectory of your project.gradlew buildWar -
Create the application home directory, e.g.
C:\app_home. -
Download and install the Tomcat 9 Windows Service Installer from the Apache Tomcat official site.
-
Go to the
bindirectory of the installed server and runtomcat9w.exewith the administrative rights in order to set Tomcat service settings:-
Set Maximum memory pool to 1024MB on the Java tab.
-
Instruct Tomcat to use UTF-8 encoding by adding
-Dfile.encoding=UTF-8to the Java Options field. -
Specify application home folder by adding the
-Dapp.home=c:/app_hometo the Java Options field.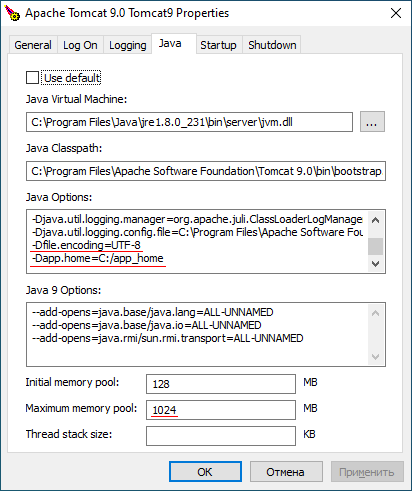
-
-
If you want to provide production database connection properties with a local file on the server, you can create a file in the
conf\Catalina\localhostsubfolder of the Tomcat server. The name of the file depends on the WAR file name, e.g.app.xmlfor single WAR andapp-core.xmlif separate WAR files are deployed. Copy contents of thecontext.xmlto this file. -
With the default configuration all application log messages are appended to the
logs/tomcat9-stdout.logfile. You have two options how to customize logging configuration of the application:-
Create the logback configuration file in the project. Specify path to this file for the
logbackConfigurationFileparameter of the buildWar task (manually or with the help of Studio WAR Settings dialog). -
Create the logging configuration file on the production server.
Copy the
logback.xmlfile from the development Tomcat (deploy/tomcat/confproject sub-folder) to the application home directory and edit thelogDirproperty in this file:<property name="logDir" value="${app.home}/logs"/>Add the following line to the Java Options field in the Tomcat 9 Windows Service settings window to specify path to the logging configuration file:
-Dlogback.configurationFile=C:/app_home/logback.xml
-
-
Copy the generated WAR file(s) to the
webappsdirectory of the Tomcat server. -
Restart the Tomcat service.
-
Open
http://localhost:8080/appin your web browser.