5.9.1.1. Managing Dynamic Attributes
Managing attributes categories and descriptions is done via special screens available in Administration > Dynamic Attributes menu.
The category browser shows the list of all registered categories.
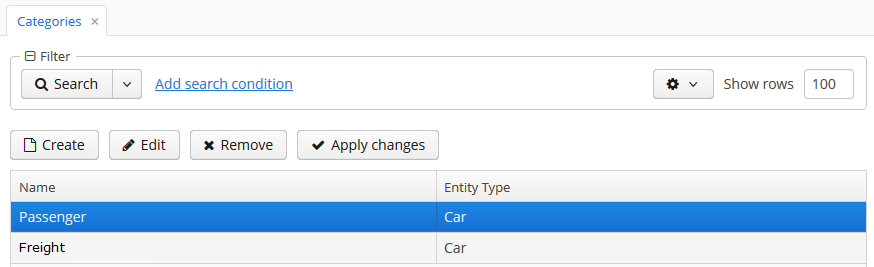
The category editor allows you to create a new category for an entity and define a set of dynamic attributes. The category name and the related entity type fields are mandatory. The Default checkbox indicates that this category will be automatically selected for a new instance of an entity implementing Categorized interface.
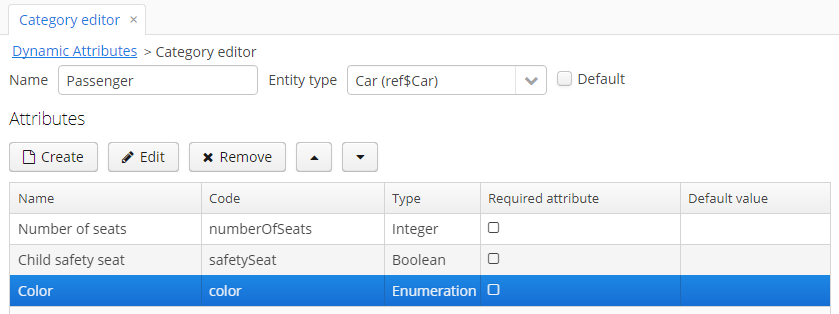
The Name localization groupbox is shown if the application supports more than one language. It enables setting the localized values of category names for each available locale.
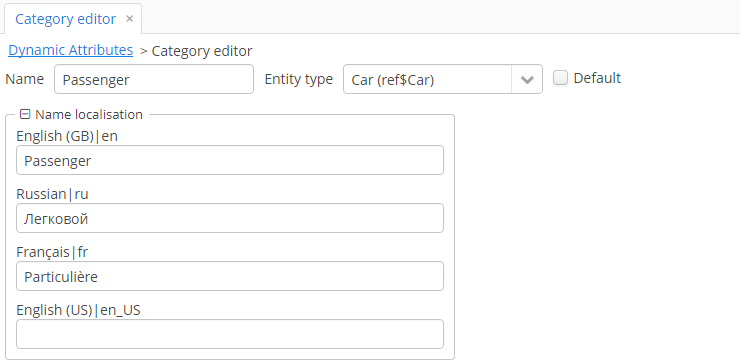
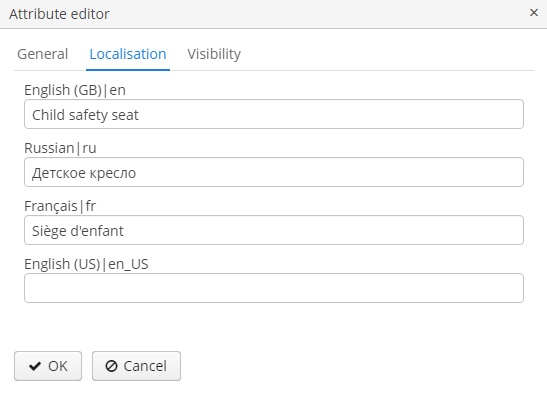
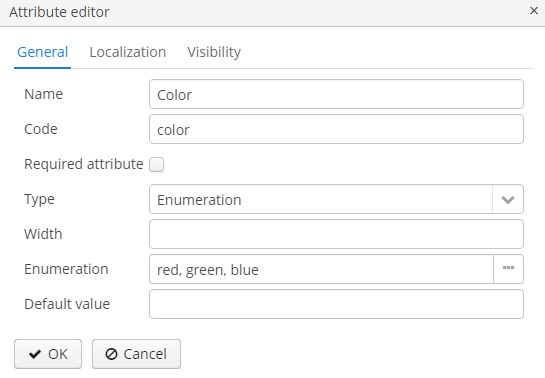
Dynamic attribute editor enables setting the name, system code, value type and the default value of the attribute.
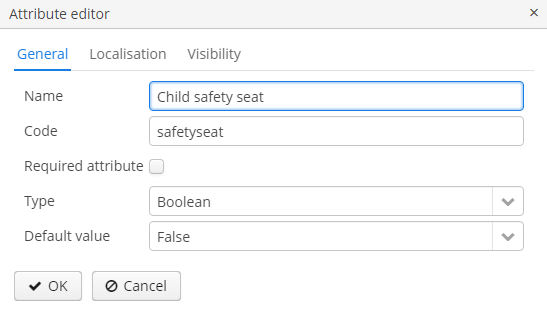
For all value types, except Boolean, there is a Width field available to set up the field width in FieldGroup in pixels or as a percentage. If the Width field is empty, its assumed value is 100%.
For all value types, except Boolean and Enumeration, there is also an Is collection checkbox available. It allows you to create multi-valued dynamic attributes of a selected type.
Localization is supported for all types of dynamic attributes:
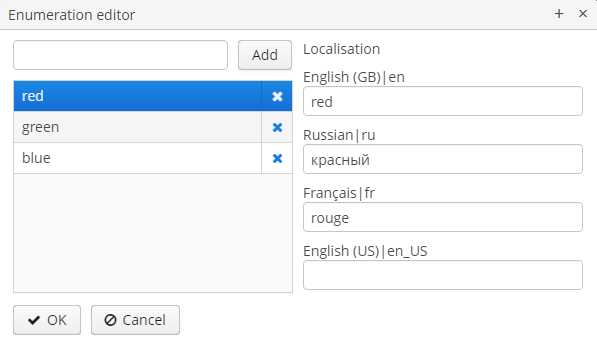
For the Enumeration value type, the set of named values is defined in the Enumeration field via the list editor.
Enumeration type
Each enumeration value can also be localized to the languages, available for the application.
Enumeration type
A dynamic attribute also has visibility settings, which define the screens where it should be displayed. By default, the attribute is invisible on any screen.
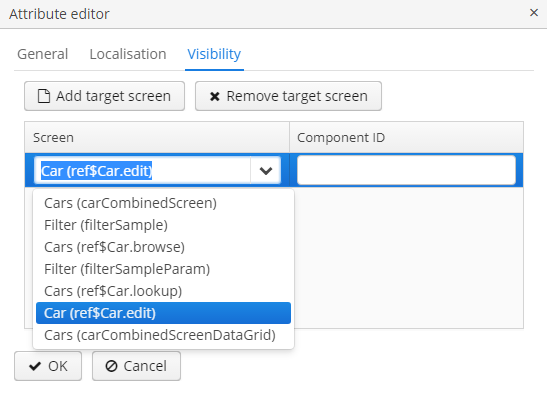
In addition to the screen, you can also specify a component in which the attribute is to appear (for example, for screens, where several FieldGroup components show the fields of the same entity).
If the attribute is marked as visible on a screen, it will automatically appear in all field groups and tables displaying entities of the corresponding type on the screen.
Access to dynamic attributes can also be restricted by user role settings. Security settings for dynamic attributes are similar to those for regular attributes.
In order for changes in attribute and visibility settings to take effect, click Apply settings in the categories browser. Changes can also be applied via Administration > JMX Console by calling the clearDynamicAttributesCache() method of the app-core.cuba:type=CachingFacade JMX bean.
The dynamic attribute added to the screen automatically by specifying visibility settings is shown below:
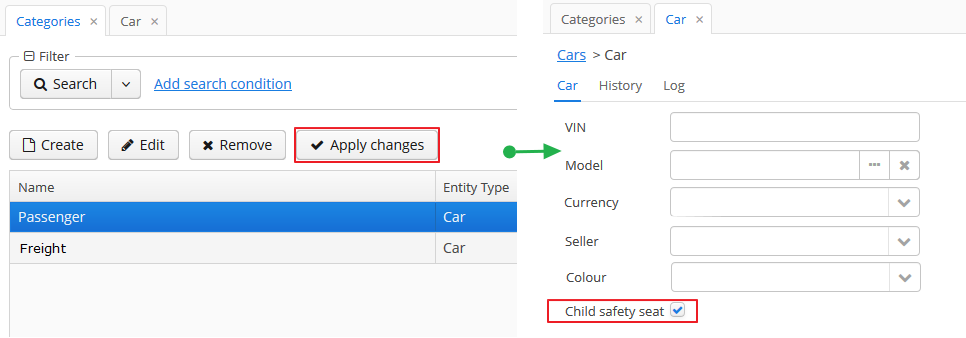
Dynamic attributes can be added to a screen manually. To do this, follow these steps:
-
In the
dsContextsection of the screen XML-descriptor, set theloadDynamicAttributesproperty totruefor a datasource that loads the entity (entities), for example:<dsContext> <datasource id="carDs" class="com.company.sample.entity.Car" view="_local" loadDynamicAttributes="true"/> </dsContext> -
Specify the dynamic attribute code with the
+prefix in thepropertyXML attribute of a component definition:<textField id="numberOfSeats" datasource="carDs" property="+numberOfSeats"/>