3.2.6. Class-Defined Template
Class-defined templates are used when it is too difficult or impossible to select data using SQL, JPQL or Groovy. They are used, for example, when the report is a result of combining several other reports.
The class defining the template must be placed in the core module and implement the com.haulmont.yarg.formatters.CustomReport interface. In the class, you need to define the createReport() method, which returns an array of bytes and takes the following input parameters:
-
report- report descriptor of thecom.haulmont.yarg.structure.Reporttype. -
rootBand- root band data of thecom.haulmont.yarg.structure.BandDatatype. -
params- map of external report parameters.
Below is an example of a simple class-defined template. It creates an HTML document showing the name of a book selected as report parameter:
package com.sample.library.report;
import com.haulmont.yarg.formatters.CustomReport;
import com.haulmont.yarg.structure.BandData;
import com.haulmont.yarg.structure.Report;
import com.sample.library.entity.Book;
import java.util.Map;
public class BookReport implements CustomReport {
@Override
public byte[] createReport(Report report, BandData rootBand, Map<String, Object> params) {
Book book = (Book) params.get("book");
String html = "<html><body>";
html += "<p>Name: " + book.getName() + "</p>";
html += "</body></html>";
return html.getBytes();
}
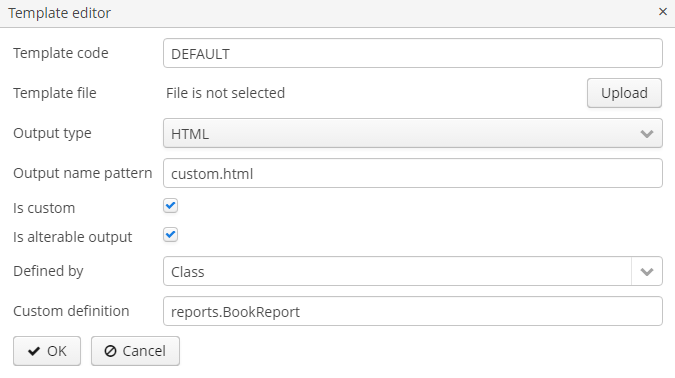
}In the template editor check the Is custom checkbox, select Class in the Defined by field and set the fully qualified name of the Java class as the custom definition: