3.5.2.4.4. Validator
Validator is designed to check values entered into visual components.
|
Validation and input type checking should be differentiated. If a given component (e.g., TextField) data type is set to anything different than string (this can happen when binding to an entity attribute or setting On the other hand, validation does not act immediately on data entry or focus loss, but rather when the component’s |
The framework contains the set of implementations for the most frequently used validators, which can be used in your project:
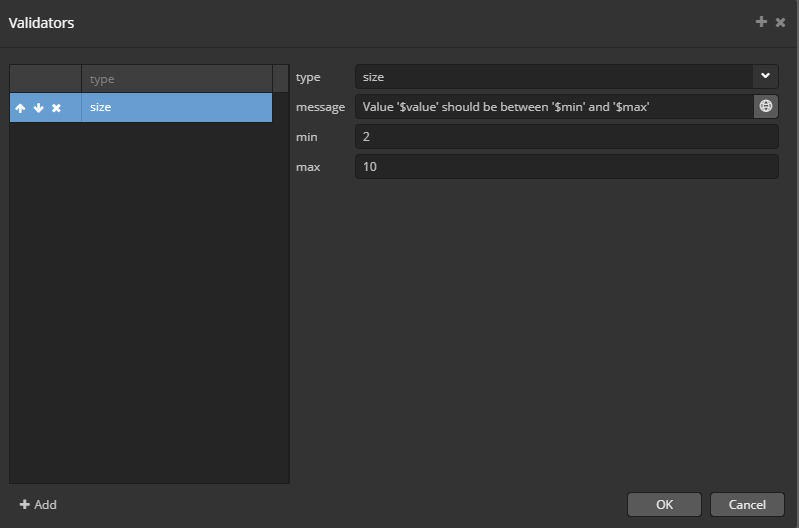
In a screen XML-descriptor, such component validators can be defined in a nested validators element. Validator can be added using CUBA Studio interface. Below is an example of adding a validator to the TextField component:
Each validator is a Prototype Bean, and if you want to use validators from Java code, you need to get them using BeanLocator.
Some of the validators use Groovy string in error message. It means that it is possible to pass parameters to the error message (e.g., $value). These parameters take account of user’s locale.
You can use a custom Java class as a validator. It should implement the Consumer interface.
In a screen XML-descriptor, a custom validator can be defined in a nested validator element.
|
If the validator is implemented as an internal class, it should be declared with a
|
A validator class can be assigned to a component not only using a screen XML-descriptor but also programmatically – by submitting a validator instance into the component’s addValidator() method.
Example of creating a validator class for zip codes:
public class ZipValidator implements Consumer<String> {
@Override
public void accept(String s) throws ValidationException {
if (s != null && s.length() != 6)
throw new ValidationException("Zip must be of 6 characters length");
}
}Example of using a zip code validator for the TextField component:
<textField id="zipField" property="zip">
<validator class="com.company.sample.web.ZipValidator"/>
</textField>Example of setting a validator programmatically in a screen controller:
zipField.addValidator(value -> {
if (value != null && value.length() != 6)
throw new ValidationException("Zip must be of 6 characters length");
});Below we consider predefined validators.
- DecimalMaxValidator
-
It checks that value is less than or equal to the specified maximum. Supported types:
BigDecimal,BigInteger,Long,Integer, andStringthat representsBigDecimalvalue with the current locale.It has the following attributes:
-
value− maximum value (required); -
inclusive− when set totrue, the value should be less than or equal to the specified maximum value. The default value istrue; -
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails. This message can contain$valueand$maxkeys for formatted output.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.decimalMaxInclusive -
validation.constraints.decimalMax
Layout descriptor usage:
<textField id="numberField" property="numberProperty"> <validators> <decimalMax value="10000" inclusive="false" message="Value '$value' cannot be greater than `$max`"/> </validators> </textField>Java code usage:
DecimalMaxValidator maxValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(DecimalMaxValidator.NAME, new BigDecimal(100)); numberField.addValidator(maxValidator); -
- DecimalMinValidator
-
It checks that value is greater than or equal to the specified minimum. Supported types:
BigDecimal,BigInteger,Long,Integer, andStringthat representsBigDecimalvalue with the current locale.It has the following attributes:
-
value− minimum value (required); -
inclusive− when set totrue, the value should be greater than or equal to the specified minimum value. The default value istrue; -
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails. This message can contain$valueand$minkeys for formatted output.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.decimalMinInclusive -
validation.constraints.decimalMin
Layout descriptor usage:
<textField id="numberField" property="numberProperty"> <validators> <decimalMin value="100" inclusive="false" message="Value '$value' cannot be less than `$min`"/> </validators> </textField>Java code usage:
DecimalMinValidator minValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(DecimalMinValidator.NAME, new BigDecimal(100)); numberField.addValidator(minValidator); -
- DigitsValidator
-
It checks that value is a number within the accepted range. Supported types:
BigDecimal,BigInteger,Long,Integer, andStringthat representsBigDecimalvalue with the current locale.It has the following attributes:
-
integer− count of numbers in the integer part (required); -
fraction− count of numbers in the fraction part (required); -
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails. This message can contain$value,$integer, and$fractionkeys for formatted output.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.digits
Layout descriptor usage:
<textField id="numberField" property="numberProperty"> <validators> <digits integer="3" fraction="2" message="Value '$value' is out of bounds ($integer digits are expected in integer part and $fraction in fractional part)"/> </validators> </textField>Java code usage:
DigitsValidator digitsValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(DigitsValidator.NAME, 3, 2); numberField.addValidator(digitsValidator); -
- FutureOrPresentValidator
-
It validates that date or time is in the future or present. It doesn’t use Groovy string, so there are no parameters you can pass to the error message. Supported types:
java.util.Date,LocalDate,LocalDateTime,LocalTime,OffsetDateTime,OffsetTime.It has the following attributes:
-
checkSeconds− when set totrue, the validator should compare date or time with seconds and nanos. The default value isfalse; -
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.futureOrPresent
Layout descriptor usage:
<dateField id="dateTimePropertyField" property="dateTimeProperty"> <validators> <futureOrPresent checkSeconds="true"/> </validators> </dateField>Java code usage:
FutureOrPresentValidator futureOrPresentValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(FutureOrPresentValidator.NAME); dateField.addValidator(futureOrPresentValidator); -
- FutureValidator
-
It validates that date or time is in the future. It doesn’t use Groovy string, so there are no parameters you can pass to the error message. Supported types:
java.util.Date,LocalDate,LocalDateTime,LocalTime,OffsetDateTime,OffsetTime.It has the following attributes:
-
checkSeconds− when set totrue, the validator should compare date or time with seconds and nanos. The default value isfalse; -
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.future
Layout descriptor usage:
<timeField id="localTimeField" property="localTimeProperty" showSeconds="true"> <validators> <future checkSeconds="true"/> </validators> </timeField>Java code usage:
FutureValidator futureValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(FutureValidator.NAME); timeField.addValidator(futureValidator); -
- MaxValidator
-
It checks that value is less than or equal to the specified maximum. Supported types:
BigDecimal,BigInteger,Long,Integer.It has the following attributes:
-
value− maximum value (required); -
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails. This message can contain$valueand$maxkeys for formatted output.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.max
Layout descriptor usage:
<textField id="numberField" property="numberProperty"> <validators> <max value="20500" message="Value '$value' must be less than or equal to '$max'"/> </validators> </textField>Java code usage:
MaxValidator maxValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(MaxValidator.NAME, 20500); numberField.addValidator(maxValidator); -
- MinValidator
-
It checks that value is greater than or equal to the specified minimum. Supported types:
BigDecimal,BigInteger,Long,Integer.It has the following attributes:
-
value− minimum value (required); -
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails. This message can contain$value, and$minkeys for formatted output.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.min
Layout descriptor usage:
<textField id="numberField" property="numberProperty"> <validators> <min value="30" message="Value '$value' must be greater than or equal to '$min'"/> </validators> </textField>Java code usage:
MinValidator minValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(MinValidator.NAME, 30); numberField.addValidator(minValidator); -
- NegativeOrZeroValidator
-
It checks that value is less than or equal 0. Supported types:
BigDecimal,BigInteger,Long,Integer,Double,Float.It has the following attributes:
-
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails. This message can contain$valuekey for formatted output. Note, thatFloatdoesn’t have its own datatype and won’t be formatted with the user’s locale.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.negativeOrZero
Layout descriptor usage:
<textField id="numberField" property="numberProperty"> <validators> <negativeOrZero message="Value '$value' must be less than or equal to 0"/> </validators> </textField>Java code usage:
NegativeOrZeroValidator negativeOrZeroValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(NegativeOrZeroValidator.NAME); numberField.addValidator(negativeOrZeroValidator); -
- NegativeValidator
-
It checks that value is strictly less than 0. Supported types:
BigDecimal,BigInteger,Long,Integer,Double,Float.It has the following attributes:
-
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails. This message can contain$valuekey for formatted output. Note, thatFloatdoesn’t have its own datatype and won’t be formatted with the user’s locale.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.negative
Layout descriptor usage:
<textField id="numberField" property="numberProperty"> <validators> <negative message="Value '$value' should be less than 0"/> </validators> </textField>Java code usage:
NegativeValidator negativeValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(NegativeValidator.NAME); numberField.addValidator(negativeValidator); -
- NotBlankValidator
-
It checks that value contains at least one non-whitespace character. It doesn’t use Groovy string, so there are no parameters you can pass to the error message. Supported type:
String.It has the following attributes:
-
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.notBlank
Layout descriptor usage:
<textField id="textField" property="textProperty"> <validators> <notBlank message="Value must contain at least one non-whitespace character"/> </validators> </textField>Java code usage:
NotBlankValidator notBlankValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(NotBlankValidator.NAME); textField.addValidator(notBlankValidator); -
- NotEmptyValidator
-
It checks that value is not
nulland not empty. Supported types:CollectionandString.It has the following attributes:
-
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails. This message can contain$valuekey for formatted output, only forStringtype.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.notEmpty
Layout descriptor usage:
<textField id="textField" property="textProperty"> <validators> <notBlank message="Value must contain at least one non-whitespace character"/> </validators> </textField>Java code usage:
NotBlankValidator notBlankValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(NotBlankValidator.NAME); textField.addValidator(notBlankValidator); -
- NotNullValidator
-
It checks that value is not
null. It doesn’t use Groovy string, so there are no parameters you can pass to the error message.It has the following attributes:
-
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.notNull
Layout descriptor usage:
<textField id="numberField" property="numberProperty"> <validators> <notNull/> </validators> </textField>Java code usage:
NotNullValidator notNullValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(NotNullValidator.NAME); numberField.addValidator(notNullValidator); -
- PastOrPresentValidator
-
It validates that date or time is in the past or present. It doesn’t use Groovy string, so there are no parameters you can pass to the error message. Supported types:
java.util.Date,LocalDate,LocalDateTime,LocalTime,OffsetDateTime,OffsetTime.It has the following attributes:
-
checkSeconds− when setting totrue, the validator should compare date or time with seconds and nanos. The default value isfalse; -
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.pastOrPresent
Layout descriptor usage:
<dateField id="dateTimeField" property="dateTimeProperty"> <validators> <pastOrPresent/> </validators> </dateField>Java code usage:
PastOrPresentValidator pastOrPresentValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(PastOrPresentValidator.NAME); numberField.addValidator(pastOrPresentValidator); -
- PastValidator
-
It validates that date or time is in the past. It doesn’t use Groovy string, so there are no parameters you can pass to the error message. Supported types:
java.util.Date,LocalDate,LocalDateTime,LocalTime,OffsetDateTime,OffsetTime.It has the following attributes:
-
checkSeconds− when setting totrue, the validator should compare date or time with seconds and nanos. The default value isfalse; -
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.past
Layout descriptor usage:
<dateField id="dateTimeField" property="dateTimeProperty"> <validators> <pastOrPresent/> </validators> </dateField>Java code usage:
PastOrPresentValidator pastOrPresentValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(PastOrPresentValidator.NAME); numberField.addValidator(pastOrPresentValidator); -
- PositiveOrZeroValidator
-
It checks that value is greater than or equal to 0. Supported types:
BigDecimal,BigInteger,Long,Integer,Double,Float.It has the following attributes:
-
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails. This message can contain$valuekey for formatted output. Note, thatFloatdoesn’t have its own datatype and won’t be formatted with the user’s locale.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.positiveOrZero
Layout descriptor usage:
<textField id="numberField" property="numberProperty"> <validators> <positiveOrZero message="Value '$value' should be greater than or equal to '0'"/> </validators> </textField>Java code usage:
PositiveOrZeroValidator positiveOrZeroValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(PositiveOrZeroValidator.NAME); numberField.addValidator(positiveOrZeroValidator); -
- PositiveValidator
-
It checks that value is strictly greater than 0. Supported types:
BigDecimal,BigInteger,Long,Integer,Double,Float.It has the following attributes:
-
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails. This message can contain$valuekey for formatted output. Note, thatFloatdoesn’t have its own datatype and won’t be formatted with the user’s locale.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.positive
Layout descriptor usage:
<textField id="numberField" property="numberProperty"> <validators> <positive message="Value '$value' should be greater than '0'"/> </validators> </textField>Java code usage:
PositiveValidator positiveValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(PositiveValidator.NAME); numberField.addValidator(positiveValidator); -
- RegexpValidator
-
It checks that
Stringvalue is matched with specified regular expression. Supported type:String.It has the following attributes:
-
regexp− a regular expression to match (required); -
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails. This message can contain$valuekey for formatted output.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.regexp
Layout descriptor usage:
<textField id="textField" property="textProperty"> <validators> <regexp regexp="[a-z]*"/> </validators> </textField>Java code usage:
RegexpValidator regexpValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(RegexpValidator.NAME, "[a-z]*"); textField.addValidator(regexpValidator); -
- SizeValidator
-
It checks that value is in a specific range. Supported types:
CollectionandString.It has the following attributes:
-
min− a minimum value (with inclusive), cannot be less than 0. The default value is 0; -
max− a maximum value (with inclusive), cannot be less than 0. The default value isInteger.MAX_VALUE; -
message− a custom message displayed to a user when validation fails. This message can contain$value(only forStringtype),$min,$maxkeys for formatted output.
Default message keys:
-
validation.constraints.collectionSizeRange -
validation.constraints.sizeRange
Layout descriptor usage:
<textField id="textField" property="textProperty"> <validators> <size min="2" max="10" message="Value '$value' should be between '$min' and '$max'"/> </validators> </textField> <twinColumn id="twinColumn"> <validators> <size min="2" max="4" message="Collection size must be between $min and $max"/> </validators> </twinColumn>Java code usage:
SizeValidator sizeValidator = beanLocator.getPrototype(SizeValidator.NAME); textField.addValidator(sizeValidator); -