3.2.1.1. Base Entity Classes
The base entity classes and interfaces are described in detail in this section.
-
Instance– declares the basic methods for working with objects of application domain:-
getting references to the object meta-class;
-
generating the instance name;
-
reading/writing attribute values by name;
-
adding listeners receiving notifications about attribute changes.
-
-
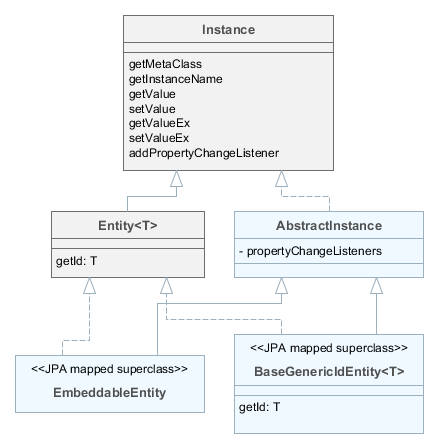
Entity– extendsInstancewith entity identifier; at the same timeEntitydoes not define the type of the identifier leaving this option to descendants. -
AbstractInstance– implements the logic of working with attribute change listeners.AbstractInstancestores the listeners inWeakReference, and if there are no external references to the added listener, it will be immediately destroyed by garbage collector. Normally, attribute change listeners are visual components and UI datasources that are always referenced by other objects, so there is no problem with listeners dropout. However, if a listener is created by application code and no objects refer to it in a natural way, it is necessary to save it in a certain object field apart from just adding it toInstance. -
BaseGenericIdEntity– base class of persistent and non-persistent entities. It implementsEntitybut does not specify the type of the identifier (i.e. the primary key) of the entity. -
EmbeddableEntity- base class of embeddable persistent entities.
Below we consider base classes recommended for inheriting your entities from. Non-persistent entities should be inherited from the same base classes as persistent ones. The framework determines if the entity is persistent or not by the file where it is registered: persistence.xml or metadata.xml.
- StandardEntity
-
Inherit from
StandardEntityif you want a standard set of features: the primary key of UUID type, the instances have information on who and when created and modified them, require optimistic locking and soft deletion.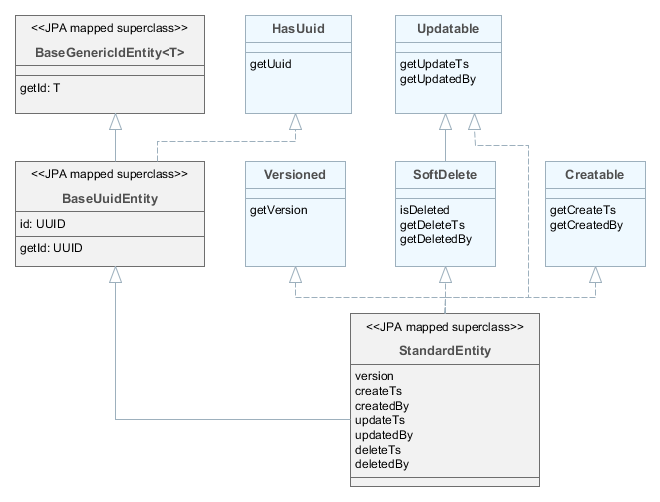
-
HasUuid– interface for entities having a globally unique identifier. -
Versioned– interface for entities supporting optimistic locking. -
Creatable– interface for entities that keep the information about when and by whom the instance was created. -
Updatable– interface for entities that keep the information about when and by whom the instance was last changed. -
SoftDelete– interface for entities supporting soft deletion.
-
- BaseUuidEntity
-
Inherit from
BaseUuidEntityif you want an entity with the primary key of UUID type but you don’t need all features ofStandardEntity. You can implement some of the interfacesCreatable,Versioned, etc. in your concrete entity class.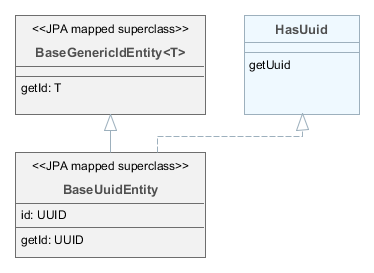
- BaseLongIdEntity
-
Inherit from
BaseLongIdEntityorBaseIntegerIdEntityif you want an entity with the primary key of theLongorIntegertype. You can implement some of the interfacesCreatable,Versioned, etc. in your concrete entity class. ImplementingHasUuidis highly recommended, as it enables some optimizations and allows you to identify your instances uniquely in a distributed environment.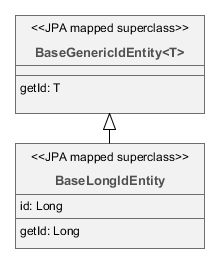
- BaseStringIdEntity
-
Inherit from
BaseStringIdEntityif you want an entity with the primary key of theStringtype. You can implement some of the interfacesCreatable,Versioned, etc. in your concrete entity class. ImplementingHasUuidis highly recommended, as it enables some optimizations and allows you to identify your instances uniquely in a distributed environment. The concrete entity class must have a string field annotated with the@IdJPA annotation.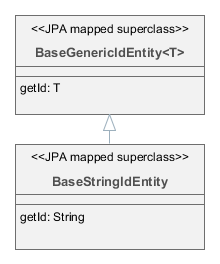
- BaseIdentityIdEntity
-
Inherit from
BaseIdentityIdEntityif you need to map the entity to a table with IDENTITY primary key. You can implement some of the interfacesCreatable,Versioned, etc. in your concrete entity class. ImplementingHasUuidis highly recommended, as it enables some optimizations and allows you to identify your instances uniquely in a distributed environment. Theidattribute of the entity (i.e.getId()/setId()methods) will be of typeIdProxywhich is designed to substitute the real identifier until it is generated by the database on insert.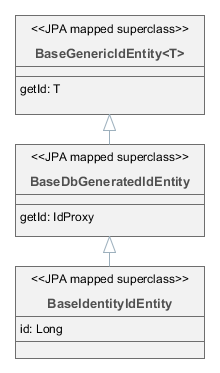
- BaseIntIdentityIdEntity
-
Inherit from
BaseIntIdentityIdEntityif you need to map the entity to a table with IDENTITY primary key ofIntegertype (compared toLonginBaseIdentityIdEntity). In other respects,BaseIntIdentityIdEntityis similar toBaseIdentityIdEntity.
- BaseGenericIdEntity
-
Inherit from
BaseGenericIdEntitydirectly if you need to map the entity to a table with a composite key. In this case, the concrete entity class must have a field of the embeddable type representing the key, annotated with the@EmbeddedIdJPA annotation.