7.6. Application Scaling
This section describes ways to scale a CUBA application that consists of the Middleware and the Web Client for increased load and stronger fault tolerance requirements.
|
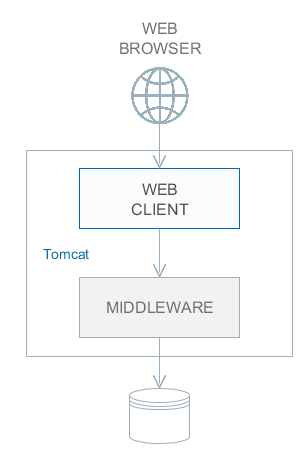
Stage 1. Both blocks are deployed on the same application server. This is the simplest option implemented by the standard fast deployment procedure. In this case, maximum data transfer performance between the Web Client and the Middleware is provided, because when the cuba.useLocalServiceInvocation application property is enabled, the Middleware services are invoked bypassing the network stack. |
|
|
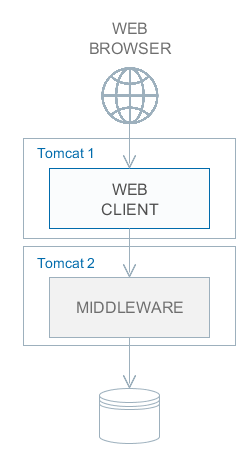
Stage 2. The Middleware and the Web Client blocks are deployed on separate application servers. This option allows you to distribute load between two application servers and use server resources better. Furthermore, in this case, the load coming from web users has smaller effect on the other processes execution. Here, the other processes mean handling other client types (for example, Desktop), running scheduled tasks and, potentially, integration tasks which are performed by the middle layer. Requirements for server resources:
In this case and when more complex deployment options are used, the Web Client’s cuba.useLocalServiceInvocation application property should be set to |
|
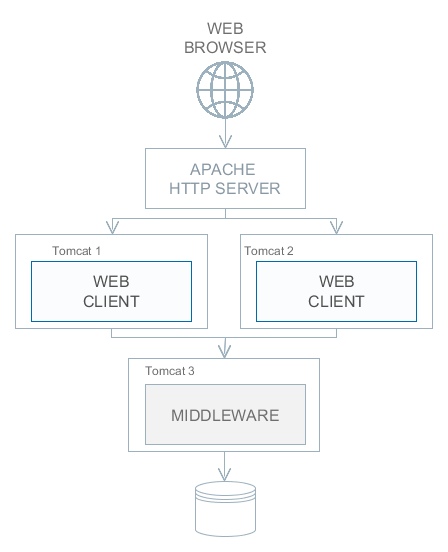
Stage 3. A cluster of Web Client servers works with one Middleware server. This option is used when memory requirements for the Web Client exceed the capabilities of a single JVM due to a large number of concurrent users. In this case, a cluster of Web Client servers (two or more) is started and user connection is performed through a Load Balancer. All Web Client servers work with one Middleware server. Duplication of Web Client servers automatically provides fault tolerance at this level. However, the replication of HTTP sessions is not supported, in case of unscheduled outage of one of the Web Client servers, all users connected to it will have to login into the application again. Configuration of this option is described in Setting up a Web Client Cluster. |
|
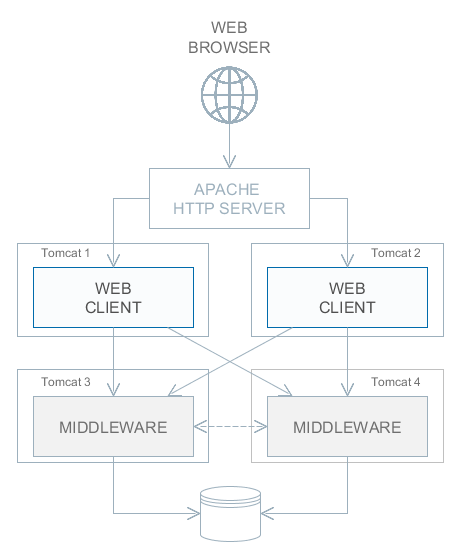
Stage 4. A cluster of Web Client servers working with a cluster of Middleware servers. This is the most powerful deployment option providing fault tolerance and load balancing for the Middleware and the Web Client. Connection of users to the Web Client servers is performed through a load balancer. The Web Client servers work with a cluster of Middleware servers. They do not need an additional load balancer – it is sufficient to determine the list of URLs for the Middleware servers in the cuba.connectionUrlList application property. Another option is to use Apache ZooKeeper Integration Add-on for dynamic discovery of middleware servers. Middleware servers exchange the information about user sessions, locks, etc. In this case, full fault tolerance of the Middleware is provided – in case of an outage of one of the servers, execution of requests from client blocks will continue on an available server without affecting users. Configuration of this option is described in Setting up a Middleware Cluster. |
|