4.1.6. Running Code on Startup
Sometimes you need to run some code on the application startup, at the moment when all application functionality is already initialized and ready to work. For this, you can use AppContext.Listener.
In this section we demonstrate how to dynamically register an entity listener on application startup. Consider the following task: a project has an Employee entity that is linked one-to-one to the platform’s User entity.
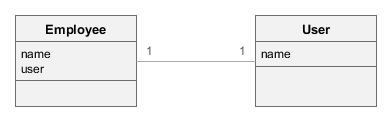
If the name attribute of the User entity is changed, for example, through a standard user management screen, the name attribute of the related Employee should change as well. This is a common task for "denormalized" data, which is typically solved using entity listeners. Our case is more complicated, since we need to track changes of the platform’s User entity, and thus we cannot add an entity listener using the @Listeners annotation. So we will add a listener dynamically using the EntityListenerManager bean on application start.
-
AppLifecycle.java - a middleware bean implementing the
AppContext.Listenerinterface with theapplicationStarted()andapplicationStopped()methods. -
UserEntityListener.java - an entity listener for the
Userentity.
As a result, the applicationStarted() method of the AppLifecycle bean will be invoked on the middleware block startup. This method registers the sample_UserEntityListener bean as an entity listener for the User entity.
The onBeforeUpdate() method of the UserEntityListener class will be invoked every time before the changes in the User instances are saved to the database. The method checks if the name attribute exists among the updated attributes. If yes, a related Employee instance is loaded and its name is updated with the new value.